-

 2025-12-02MEGA Series Zinc-Aluminum-Magnesium (ZAM) High-Strength Steel Formwork: A Practical and Easy Guide for the Construction & Formwork IndustryREAD IT >
2025-12-02MEGA Series Zinc-Aluminum-Magnesium (ZAM) High-Strength Steel Formwork: A Practical and Easy Guide for the Construction & Formwork IndustryREAD IT > -


-


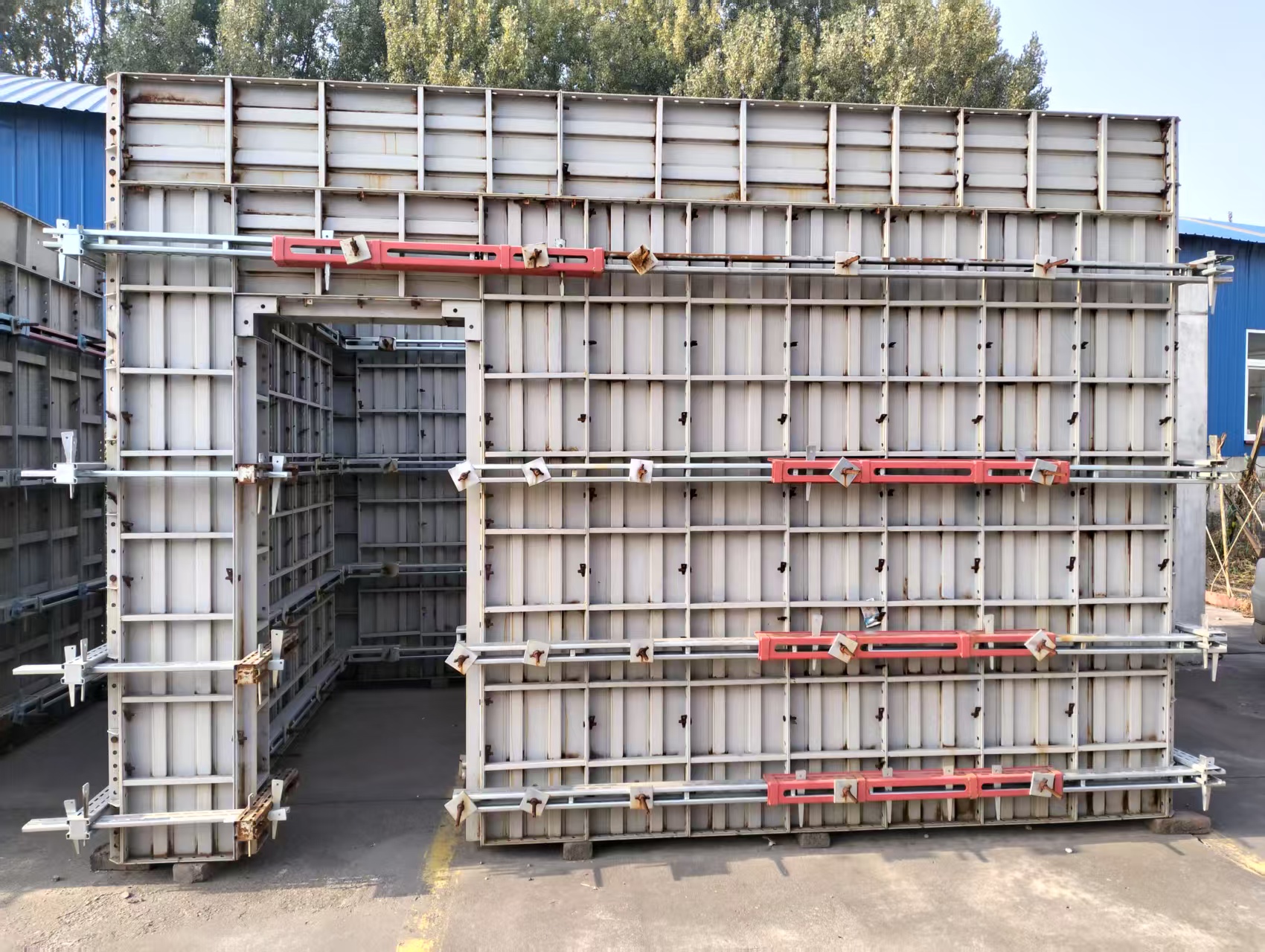
In construction, the strength, safety, and longevity of scaffolding and formwork systems rely heavily on the processes behind their manufacturing—particularly welding and galvanizing. These two treatments form the structural and protective backbone of steel-based components used across a variety of job sites, from residential high-rises to large infrastructure projects.
This article provides a clear overview of the core welding and galvanizing methods applied in the industry today, their advantages, and what best practices look like when aiming for durable and high-performing systems.
1.Why Welding and Galvanizing Are Important
Steel components exposed to dynamic loads and harsh environments require more than just good design—they need solid structural joints and long-term corrosion protection. Welding joins critical parts such as scaffolding ledgers, verticals, and planks into stable, load-bearing assemblies. Galvanizing shields those components from moisture, chemicals, and abrasion, preventing premature rust and extending service life.
Together, these processes help ensure construction systems stay safe and reliable, even after years of use.
2.Typical Components That Require These Processes
Scaffolding and formwork components undergo different combinations of welding and surface treatment, depending on their use case:
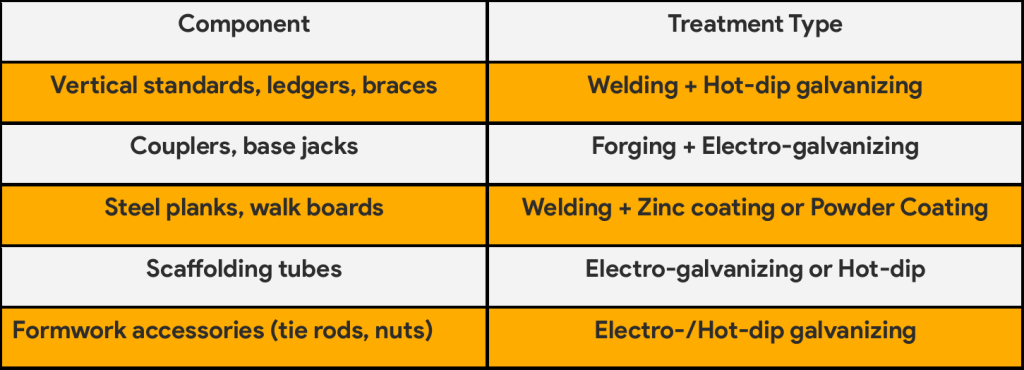
The treatment must match both mechanical requirements and environmental exposure, such as indoors vs. outdoors use.
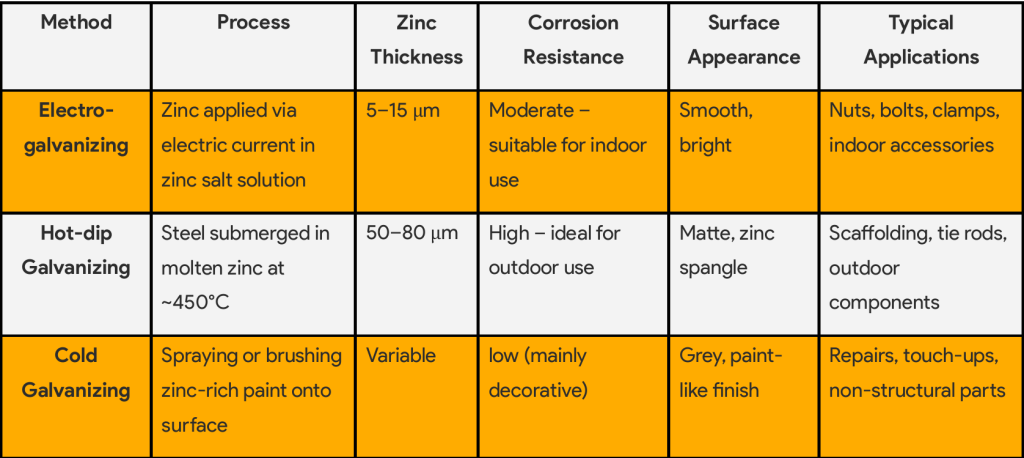
3.Comparison of Galvanizing Methods
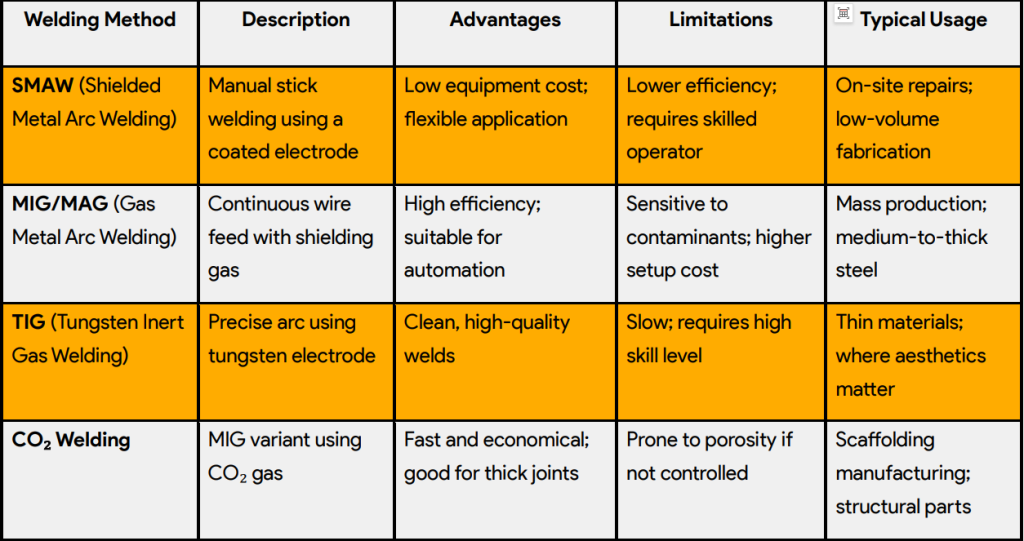
4.Comparison of Common Welding Methods
5.Challenges in CO₂ Welding and How Manufacturers Manage Risk
Among the various welding techniques used in scaffolding production, CO₂ welding remains widely adopted due to its speed and cost-efficiency. However, this method comes with a known risk: weld porosity. These are microscopic holes caused by trapped gas in the weld pool, often invisible to the naked eye. If left untreated, these pores can trap acid during the pre-galvanizing cleaning process (acid pickling), making it difficult to fully remove all residues.

When galvanizing occurs over these flawed areas, acid residue may remain sealed beneath the zinc layer, triggering localized corrosion over time. This can lead to unexpected rusting, reduced load-bearing performance, and ultimately a shortened product lifespan.
At Sampmax, this issue is proactively addressed through a dual-layer control strategy:
• Automatic CO₂ welding ensures consistent penetration and minimizes porosity. Manual repair if pores or defects are found, ensuring solid and clean welds
• Non-destructive testing (NDT) and targeted inspections identify and eliminate hidden flaws before surface treatment.
• Post-weld components go through a standardized pickling, cleaning, and passivation process, ensuring no acid remains before galvanizing.
By maintaining strict control over these steps, Sampmax significantly reduces the likelihood of corrosion-related defects, even in products used under harsh outdoor conditions.

6. Quality Assurance and Certification System at Sampmax
Sampmax implements a comprehensive quality control framework from raw material sourcing to final shipment. This system ensures that all scaffolding and formwork products meet international standards while maintaining consistency and long-term performance.
Key Elements of Our Quality System:
• Raw Material Verification
All steel components are produced using Q235 or Q355-grade steel, backed by mill test certificates and third-party verification when required.
• Production Oversight
Welding, cutting, and shaping processes are governed by a combination of automated equipment and trained operators, following defined work instructions.
• Surface Treatment Compliance
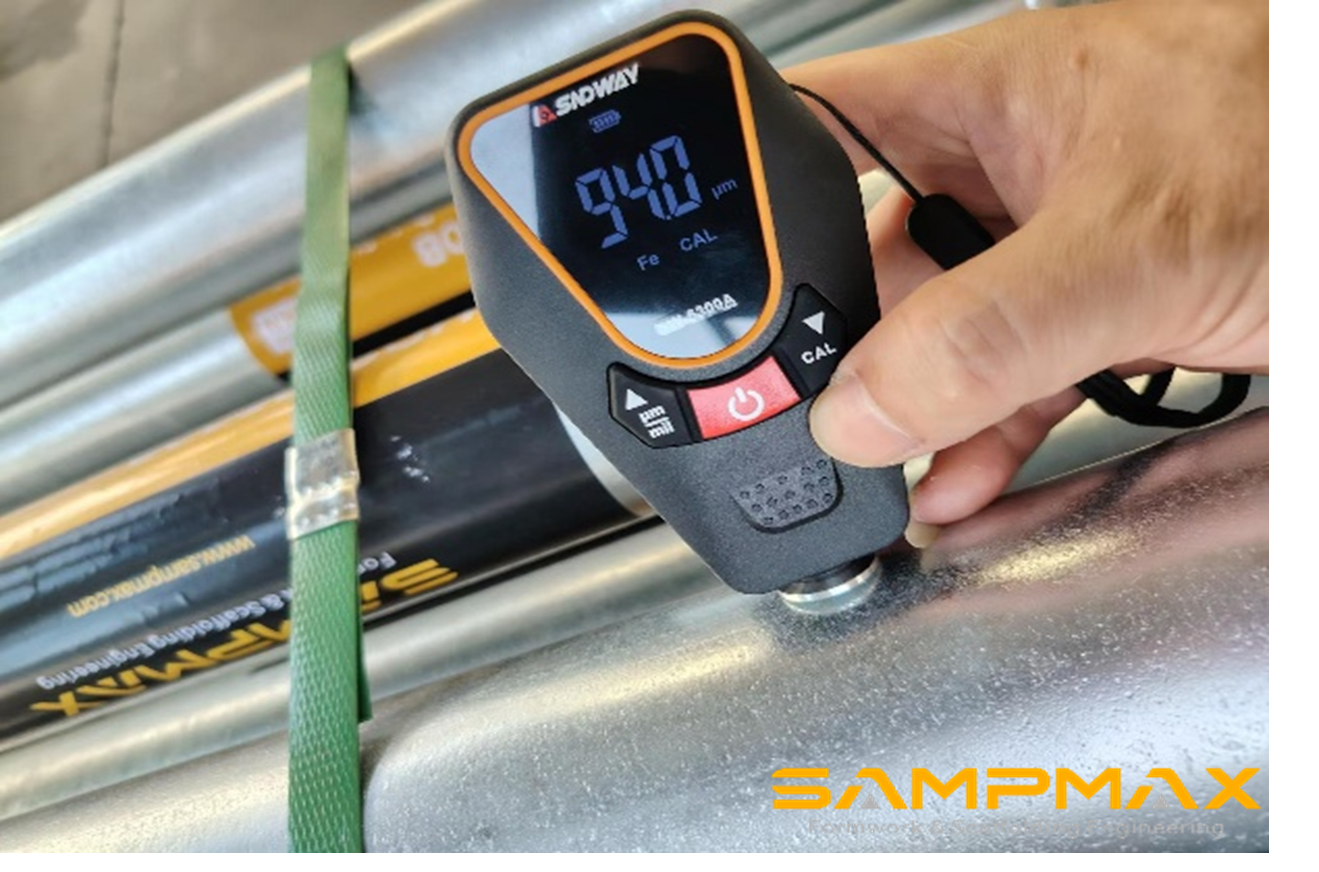
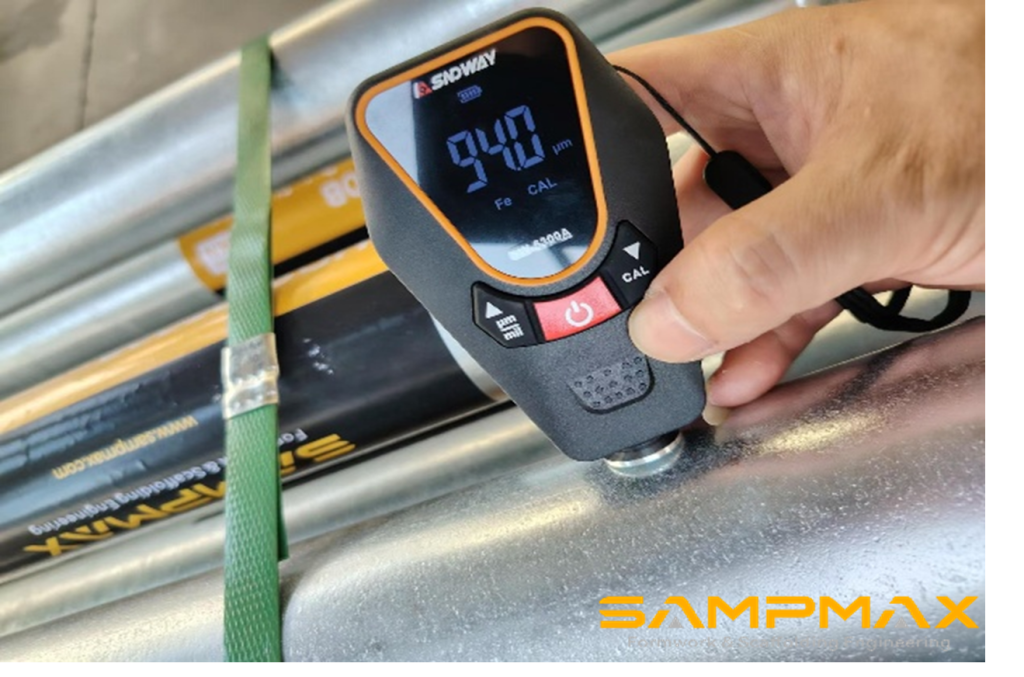
Both electro-galvanizing and hot-dip galvanizing processes are applied based on product type, and all coatings are tested for thickness and adhesion.
• Pre-shipment Testing
Each production lot is tested for: Dimensional tolerance , Zinc layer thickness, Load-bearing capacity, Salt spray resistance
• Third-party Testing Available
Upon request, Sampmax provides SGS, TUV, or other international inspection reports, reinforcing the trust of clients in high-standard regions such as Europe, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia.

Through this systematic approach, Sampmax helps reduce long-term project risks, supports contractor efficiency, and delivers a level of confidence that goes beyond the steel itself.

